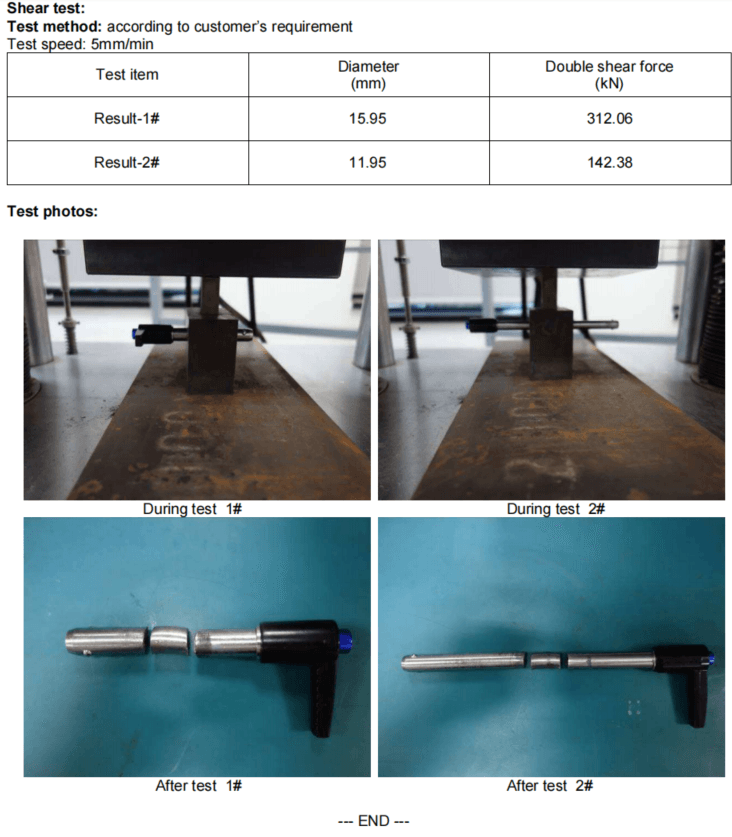
The primary factors affecting the shear strength of quick-release pins are the material of the pin's main body。
The functional part of the quick-release pin utilizes steel balls within the main body to secure the functional area. During use, this functional area exerts a radial cutting force on the main body of the quick-release pin. This is commonly referred to as shear force. Therefore, the shear strength depends on two factors of the main body: first, the material of the main body; second, the diameter of the hole through which the inner pin passes in the center of the main body.
The standard materials for quick-release pins include stainless steel 303, stainless steel 304, stainless steel 316, stainless steel 17-4, and stainless steel 440C. Carbon steel is rarely used for quick-release pins because its manufacturing process is relatively complex. Additionally, carbon steel surfaces are prone to rust, so surface treatment is required after heat treatment.Furthermore, carbon steel is prone to deformation during heat treatment, and while it achieves sufficient hardness after heat treatment, its toughness is relatively poor. Therefore, carbon steel is generally not used as the main material for quick-release pins. However, stainless steel 420 or 430 can be used for the inner pins of quick-release pins, as the inner pins require lower toughness specifications.High hardness is required. During heat treatment, a protective layer can be formed on the surface through vacuum (nitrogen-filled) treatment, thereby preventing rusting.